Spring官网:https://spring.io/
参考视频:
源码仓库:muyoukule/accidence-spring (github.com)
1. Spring IoC注解式开发
1.1 回顾注解
注解的存在主要是为了简化XML的配置。
我们来回顾一下:
- 第一:注解怎么定义,注解中的属性怎么定义?
- 第二:注解怎么使用?
- 第三:通过反射机制怎么读取注解?
注解怎么定义,注解中的属性怎么定义?
自定义注解
1
2
3
4
5
| @Target(value = {ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(value = RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Component {
String value();
}
|
以上是自定义了一个注解:Component
该注解上面修饰的注解包括:Target 注解和 Retention 注解,这两个注解被称为元注解。
Target 注解用来设置 Component 注解可以出现的位置,以上代表表示 Component 注解只能用在类和接口上。
Retention 注解用来设置 Component 注解的保持性策略,以上代表 Component 注解可以被反射机制读取。
String value(); 是 Component 注解中的一个属性。该属性类型 String ,属性名是 value 。
注解怎么使用?
1
2
3
| @Component(value = "userBean")
public class User {
}
|
用法简单,语法格式:@注解类型名(属性名=属性值, 属性名=属性值, 属性名=属性值……)
userBean 为什么使用双引号括起来,因为 value 属性是 String 类型,字符串。
另外如果属性名是 value ,则在使用的时候可以省略属性名,例如:
1
2
3
| @Component("userBean")
public class User {
}
|
通过反射机制怎么读取注解?
接下来,我们来写一段程序,当 Bean 类上有 Component 注解时,则实例化 Bean 对象,如果没有,则不实例化对象。
我们准备两个 Bean ,一个上面有注解,一个上面没有注解。
1
2
3
4
5
6
| @Component("userBean")
public class User {
}
public class Vip {
}
|
假设我们现在只知道包名:com.muyoukule.bean 。至于这个包下有多少个 Bean 我们不知道。哪些 Bean 上有注解,哪些 Bean 上没有注解,这些我们都不知道,如何通过程序全自动化判断。
a. 反射解析注解
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| public class ComponentScan {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Map<String, Object> beanMap = new HashMap<>();
String packageName = "com.muyoukule.Bean";
String path = packageName.replaceAll("\\.", "/");
URL url = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader().getResource(path);
File file = new File(url.getPath());
File[] files = file.listFiles();
Arrays.stream(files).forEach(f -> {
String className = packageName + "." + f.getName().split("\\.")[0];
try {
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName(className);
if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Component.class)) {
Component component = clazz.getAnnotation(Component.class);
String beanId = component.value();
Object bean = clazz.newInstance();
beanMap.put(beanId, bean);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
System.out.println(beanMap);
}
}
|
b. 执行结果
1
| {userBean=com.muyoukule.Bean.User@27fa135a}
|
注:如果项目存放路径有中文或者空格可能会报空指针异常
1.2 声明Bean的注解
负责声明 Bean 的注解,常见的包括四个:
@Component@Controller@Service@Repository
源码如下:
@Component 注解
1
2
3
4
5
| @Target(value = {ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(value = RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Component {
String value();
}
|
@Controller 注解
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| @Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Component
public @interface Controller {
@AliasFor(
annotation = Component.class
)
String value() default "";
}
|
@Service 注解
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| @Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Component
public @interface Service {
@AliasFor(
annotation = Component.class
)
String value() default "";
}
|
@Repository 注解
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| @Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Component
public @interface Repository {
@AliasFor(
annotation = Component.class
)
String value() default "";
}
|
通过源码可以看到,@Controller 、@Service 、@Repository 这三个注解都是 @Component 注解的别名。
也就是说:这四个注解的功能都一样。用哪个都可以。
只是为了增强程序的可读性,建议:
- 控制器类上使用:Controller
- Service类上使用:Service
- Dao类上使用:Repository
他们都是只有一个 value 属性。value属性用来指定 bean 的 id,也就是 bean 的名字。
1.3 Spring注解的使用
如何使用以上的注解呢?
- 加入aop的依赖
- 在配置文件中添加
context 命名空间
- 在配置文件中指定扫描的包
- 在Bean类上使用注解
a. 加入aop的依赖:
我们可以看到当加入 spring-context 依赖之后,会关联加入 aop 的依赖。所以这一步不用做。

b. 在配置文件 spring.xml 中添加context命名空间
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
</beans>
|
c. 在配置文件 spring.xml 中指定要扫描的包
1
| <context:component-scan base-package="com.muyoukule.Bean"/>
|
d. 在Bean类上使用注解
这里一定要注意是使用 org.springframework.stereotype 包下的 @Component ,不是上面自定义的@Component 😢
1
2
3
| @Component(value = "userBean")
public class User {
}
|
e. 编写测试程序
1
2
3
4
5
6
| @Test
public void testBean() {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
User userBean = applicationContext.getBean("userBean", User.class);
System.out.println(userBean);
}
|
f. 执行结果
1
| com.muyoukule.Bean.User@a43ce46
|
如果注解的属性名是value,那么value是可以省略的。
如果把value属性彻底去掉,spring会被 Bean 自动取名,并且默认名字的规律是:Bean类名首字母小写即可。
1
2
3
| @Component
public class BankDao {
}
|
也就是说,这个 BankDao 的 bean 的名字为:bankDao
1
| com.muyoukule.Bean.BankDao@2320fa6f
|
如果是多个包有两种解决方案:
- 在配置文件中指定多个包,用逗号隔开。
- 指定多个包的共同父包。
逗号(英文)的方式
a. 创建一个新的包:Bean2,定义一个Bean类Order
1
2
3
| @Component
public class Order {
}
|
b. 配置文件 spring.xml 中修改
1
2
3
4
|
<context:component-scan base-package="com.muyoukule"/>
|
c. 测试
1
2
| com.muyoukule.Bean.BankDao@37052337
com.muyoukule.Bean2.Order@2320fa6f
|
1.4 选择性实例化Bean
假设在某个包下有很多 Bean,有的 Bean上 标注了 @Component,有的标注了 @Controller,有的标注了 @Service,有的标注了 @Repository,现在由于某种特殊业务的需要,只允许其中所有的 @Controller 参与 Bean 管理,其他的都不实例化。这应该怎么办呢?
a. 为了方便,将这几个类都定义到同一个java源文件中
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
| @Component
public class A {
public A() {
System.out.println("A的无参数构造方法执行");
}
}
@Controller
class B {
public B() {
System.out.println("B的无参数构造方法执行");
}
}
@Service
class C {
public C() {
System.out.println("C的无参数构造方法执行");
}
}
@Repository
class D {
public D() {
System.out.println("D的无参数构造方法执行");
}
}
@Controller
class E {
public E() {
System.out.println("E的无参数构造方法执行");
}
}
@Controller
class F {
public F() {
System.out.println("F的无参数构造方法执行");
}
}
|
b. 只想实例化 Bean3 包下的 @Controller。配置文件这样写:
1
2
3
| <context:component-scan base-package="com.muyoukule.Bean3" use-default-filters="false">
<context:include-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller"/>
</context:component-scan>
|
use-default-filters="true" 表示:使用 spring 默认的规则,只要有 @Component 、@Controller 、@Service 、@Repository 中的任意一个注解标注,则进行实例化。
use-default-filters="false" 表示:不再 spring 默认实例化规则,即使有 @Component 、@Controller 、@Service 、@Repository 这些注解标注,也不再实例化。
<context:include-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller"/> 表示只有@Controller 进行实例化
c. 测试程序
1
2
3
4
| @Test
public void testChoose() {
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
}
|
d. 执行结果
1
2
3
| B的无参数构造方法执行
E的无参数构造方法执行
F的无参数构造方法执行
|
也可以将 use-default-filters 设置为 true(不写就是true),并且采用 exclude-filter 方式排出哪些注解标注的 Bean 不参与实例化:
1
2
3
4
5
| <context:component-scan base-package="com.muyoukule.Bean3">
<context:exclude-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Repository"/>
<context:exclude-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Service"/>
<context:exclude-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller"/>
</context:component-scan>
|
1.5 负责注入的注解
@Component 、@Controller 、@Service 、@Repository 这四个注解是用来声明 Bean 的,声明后这些 Bean 将被实例化。接下来我们看一下,如何给 Bean 的属性赋值。给Bean属性赋值需要用到这些注解:
@Value 、@Autowired 、@Qualifier 、@Resource
1.5.1 @Value
属性的类型是简单类型,可以使用 @Value 注解进行注入
a. 创建如下类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| @ToString
@Component
public class User {
@Value(value = "zhangsan")
private String name;
@Value("20")
private int age;
}
|
b. 开启包扫描
1
| <context:component-scan base-package="com.muyoukule.Bean4"/>
|
c. 测试
1
2
3
4
5
6
| @Test
public void testValue() {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
Object user = applicationContext.getBean("user");
System.out.println(user);
}
|
d. 执行测试程序
1
| User(name=zhangsan, age=20)
|
通过以上代码可以发现,我们并没有给属性提供 setter 方法,但仍然可以完成属性赋值。
提供 setter 方法,并且在 setter 方法上添加 @Value 注解,也可以完成注入
a. 修改类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| @ToString
@Component
public class User {
private String name;
private int age;
@Value("李四")
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Value("30")
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
|
b. 执行测试程序
为了简化代码,以后我们一般不提供 setter 方法,直接在属性上使用 @Value 注解完成属性赋值。
也能够通过构造方法完成注入
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| @ToString
@Component
public class User {
private String name;
private int age;
public User(@Value("隔壁老王") String name, @Value("33") int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
|
通过测试得知:@Value 注解可以出现在属性上、setter 方法上、构造方法的形参上。
1.5.2 @Autowired与@Qualifier
@Autowired 注解可以用来注入非简单类型。被翻译为:自动连线的,或者自动装配。
单独使用 @Autowired 注解,默认根据类型装配。【默认是 byType 】
看一下 @Autowired源码
1
2
3
4
5
6
| @Target({ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR, ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.PARAMETER, ElementType.FIELD, ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface Autowired {
boolean required() default true;
}
|
源码中有两处需要注意:
在属性上使用 @Autowired 注解
a. 创建如下类
UserDao接口
1
2
3
| public interface UserDao {
void insert();
}
|
UserDao实现类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| @Repository
public class UserDaoForMySQL implements UserDao {
@Override
public void insert() {
System.out.println("正在向mysql数据库插入User数据...");
}
}
|
UserService
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| @Service
public class UserService {
@Autowired
private UserDao userDao;
public void save() {
userDao.insert();
}
}
|
b. 配置包扫描
1
| <context:component-scan base-package="com.muyoukule.Dao,com.muyoukule.Service"/>
|
c. 测试程序
1
2
3
4
5
6
| @Test
public void testAutowired() {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
UserService userService = applicationContext.getBean("userService", UserService.class);
userService.save();
}
|
d. 结果
在setter方法使用 @Autowired 注解
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| @Service
public class UserService {
private UserDao userDao;
@Autowired
public void setUserDao(UserDao userDao) {
this.userDao = userDao;
}
public void save() {
userDao.insert();
}
}
|
在构造方法使用 @Autowired 注解
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| @Service
public class UserService {
private UserDao userDao;
@Autowired
public UserService(UserDao userDao) {
this.userDao = userDao;
}
public void save() {
userDao.insert();
}
}
|
只在构造方法的形参使用 @Autowired 注解
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| @Service
public class UserService {
private UserDao userDao;
public UserService(@Autowired UserDao userDao) {
this.userDao = userDao;
}
public void save() {
userDao.insert();
}
}
|
当有参数的构造方法只有一个时,@Autowired 注解可以省略
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| @Service
public class UserService {
private UserDao userDao;
public UserService(UserDao userDao) {
this.userDao = userDao;
}
public void save() {
userDao.insert();
}
}
|
运行结果均为:
如果有多个构造方法,@Autowired 肯定是不能省略的
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| @Service
public class UserService {
private UserDao userDao;
public UserService(UserDao userDao) {
this.userDao = userDao;
}
public UserService() {
}
public void save() {
userDao.insert();
}
}
|
执行结果
到此为止,我们已经清楚 @Autowired 注解可以出现在哪些位置了。
@Autowired 注解默认是 byType 进行注入的,也就是说根据类型注入的,如果以上程序中,UserDao 接口还有另外一个实现类,会出现问题吗?
UserDaoForOracle ,接口另一个实现类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| @Repository
public class UserDaoForOracle implements UserDao {
@Override
public void insert() {
System.out.println("正在向Oracle数据库插入User数据...");
}
}
|
运行测试,程序报错
1
| No qualifying bean of type 'com.muyoukule.Dao.UserDao' available: expected single matching bean but found 2: userDaoForMySQL,userDaoForOracle
|
可以通过 byName ,根据名称进行装配解决这个问题。
@Autowired 注解和 @Qualifier 注解联合起来才可以根据名称进行装配,在 @Qualifier 注解中指定 Bean 名称
UserDaoForOracle
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| @Repository
public class UserDaoForOracle implements UserDao {
@Override
public void insert() {
System.out.println("正在向Oracle数据库插入User数据...");
}
}
|
UserService
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| @Service
public class UserService {
private UserDao userDao;
@Autowired
@Qualifier("userDaoForOracle")
public void setUserDao(UserDao userDao) {
this.userDao = userDao;
}
public void save() {
userDao.insert();
}
}
|
执行结果
总结:
@Autowired 注解可以出现在:属性上、构造方法上、构造方法的参数上、setter方法上。- 当带参数的构造方法只有一个,
@Autowired 注解可以省略。
@Autowired 注解默认根据类型注入。如果要根据名称注入的话,需要配合 @Qualifier 注解一起使用。
1.5.3 @Resource
@Resource 注解也可以完成非简单类型注入。那它和 @Autowired 注解有什么区别?
@Resource 注解是 JDK 扩展包中的,也就是说属于 JDK 的一部分。所以该注解是标准注解,更加具有通用性。(JSR-250标准中制定的注解类型。JSR是Java规范提案。)@Autowired 注解是 Spring 框架自己的。@Resource 注解默认根据名称装配 byName,未指定 name 时,使用属性名作为 name。通过 name 找不到的话会自动启动通过类型 byType 装配。@Autowired 注解默认根据类型装配 byType,如果想根据名称装配,需要配合 @Qualifier 注解一起用。@Resource 注解用在属性上、setter 方法上。@Autowired 注解用在属性上、setter 方法上、构造方法上、构造方法参数上。
@Resource 注解属于 JDK 扩展包,所以不在 JDK 当中,需要额外引入以下依赖:【如果是JDK8的话不需要额外引入依赖。高于JDK11或低于JDK8需要引入以下依赖。】
Spring6+版本
1
2
3
4
5
| <dependency>
<groupId>jakarta.annotation</groupId>
<artifactId>jakarta.annotation-api</artifactId>
<version>2.1.1</version>
</dependency>
|
一定要注意:如果你用 Spring6,要知道 Spring6 不再支持 JavaEE,它支持的是 JakartaEE9。(Oracle 把 JavaEE贡献给 Apache 了,Apache 把 JavaEE 的名字改成 JakartaEE 了,大家之前所接触的所有的 javax.* 包名统一修改为 jakarta.* 包名了。)
Spring5-版本
1
2
3
4
5
| <dependency>
<groupId>javax.annotation</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.annotation-api</artifactId>
<version>1.3.2</version>
</dependency>
|
添加依赖,使用 @Resource 注解
a. 给这个 UserDaoForOracle 起名 xyz
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| @Repository("xyz")
public class UserDaoForOracle implements UserDao {
@Override
public void insert() {
System.out.println("正在向Oracle数据库插入User数据...");
}
}
|
b. 在UserService中使用 @Resource 注解根据 name 注入
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| @Service
public class UserService {
@Resource(name = "xyz")
private UserDao userDao;
public void save() {
userDao.insert();
}
}
|
c. 执行测试程序
当 @Resource 注解使用时没有指定name的时候,还是根据 name 进行查找,这个 name 是属性名
a. 把 UserDaoForOracle 的名字 xyz 修改为 userDao,让这个 Bean 的名字和 UserService 类中的 UserDao 属性名一致
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| @Repository("userDao")
public class UserDaoForOracle implements UserDao {
@Override
public void insert() {
System.out.println("正在向Oracle数据库插入User数据...");
}
}
|
b. UserService类中 @Resource 注解并没有指定 name
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| @Service
public class UserService {
@Resource
private UserDao userDao;
public void save() {
userDao.insert();
}
}
|
c. 执行测试程序
把 UserService 类中的属性名修改一下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| @Service
public class UserService {
@Resource
private UserDao userDao2;
public void save() {
userDao2.insert();
}
}
|
执行结果,程序报错
1
| No qualifying bean of type 'com.muyoukule.Dao.UserDao' available: expected single matching bean but found 2: userDaoForMySQL,userDao
|
根据异常信息得知:当通过 name 找不到的时候,自然会启动 byType 进行注入。以上的错误是因为 UserDao 接口下有两个实现类导致的。所以根据类型注入就会报错。
@Resource 注解可以在 setter 方法上使用
UserService添加 setter 方法并使用注解标注
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| @Service
public class UserService {
private UserDao userDao;
@Resource
public void setUserDao(UserDao userDao) {
this.userDao = userDao;
}
public void save() {
userDao.insert();
}
}
|
注意这个 setter 方法的方法名,setUserDao 去掉 set 之后,将首字母变小写 userDao,userDao 就是 name
也可以指定 name
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| @Service
public class UserService {
private UserDao userDao;
@Resource(name = "userDaoForMySQL")
public void setUserDao(UserDao userDao) {
this.userDao = userDao;
}
public void save(){
userDao.insert();
}
}
|
执行结果
总结:
@Resource 注解:默认 byName 注入,没有指定 name 时把属性名当做 name,根据 name 找不到时,才会 byType 注入。byType 注入时,某种类型的 Bean 只能有一个。
1.6 全注解式开发
上面已经可以使用注解来配置 bean ,但是依然有用到配置文件,在配置文件中对包进行了扫描,Spring 在3.0版已经支持纯注解开发
- Spring3.0开启了纯注解开发模式,使用 Java 类替代配置文件,开启了 Spring 快速开发赛道,具体如何实现?
所谓的全注解开发就是不再使用 spring 配置文件了。写一个配置类来代替配置文件。
思路分析
实现思路为:
- 将配置文件
spring.xml 删除掉,使用类来替换。
实现步骤
a. 创建一个配置类
创建一个配置类 SpringConfig
1
2
| public class SpringConfig {
}
|
b. 标识该类为配置类
在配置类上添加 @Configuration 注解,将其标识为一个配置类,替换 spring.xml
1
2
3
| @Configuration
public class SpringConfig {
}
|
c. 用注解替换包扫描配置
在配置类上添加包扫描注解 @ComponentScan 替换 <context:component-scan base-package=""/>
1
2
3
4
| @Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.muyoukule")
public class SpringConfig {
}
|
d. 编写测试程序:不再 new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext() 对象了
1
2
3
4
5
6
| @Test
public void testNoXml() {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
UserService userService = applicationContext.getBean("userService", UserService.class);
userService.save();
}
|
e. 执行结果
至此,纯注解开发的方式就已经完成了,主要内容包括:
Java类替换 Spring 核心配置文件
@Configuration 注解用于设定当前类为配置类
@ComponentScan 注解用于设定扫描路径,此注解只能添加一次,多个数据请用数组格式
1
| @ComponentScan({"com.muyoukule.service","com.muyoukule.dao"})
|
读取 Spring 核心配置文件初始化容器对象切换为读取 Java 配置类初始化容器对象
1
2
3
4
|
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
ApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
|
1.7 IOC/DI注解开发管理第三方bean
准备环境
a. 新建spring_009模块
b. pom.xml 添加 Spring 的依赖
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| <dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.3.27</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
|
c. 添加一个配置类 SpringConfig
1
2
3
| @Configuration
public class SpringConfig {
}
|
d. 添加BookDao、BookDaoImpl类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| public interface BookDao {
public void save();
}
@Repository
public class BookDaoImpl implements BookDao {
public void save() {
System.out.println("book dao save ...");
}
}
|
e. 创建运行类App
1
2
3
4
5
| public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
}
}
|
1.7.1 注解开发管理第三方bean
在上述环境中完成对 Druid 数据源的管理
a. 导入对应的 jar 包
1
2
3
4
5
| <dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.2.15</version>
</dependency>
|
b. 在配置类中添加一个方法
注意该方法的返回值就是要创建的 Bean 对象类型
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| @Configuration
public class SpringConfig {
public DataSource dataSource() {
DruidDataSource ds = new DruidDataSource();
ds.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
ds.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring_db");
ds.setUsername("root");
ds.setPassword("root");
return ds;
}
}
|
c. 在方法上添加 @Bean 注解
@Bean 注解的作用是将方法的返回值制作为 Spring 管理的一个 bean 对象
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| @Configuration
public class SpringConfig {
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource() {
DruidDataSource ds = new DruidDataSource();
ds.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
ds.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring_db");
ds.setUsername("root");
ds.setPassword("root");
return ds;
}
}
|
**注意:不能使用 DataSource ds = new DruidDataSource() **,因为 DataSource 接口中没有对应的 setter 方法来设置属性。
d. 从IOC容器中获取对象并打印
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
DataSource dataSource = ctx.getBean(DataSource.class);
System.out.println(dataSource);
}
}
|
e. 结果
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| {
CreateTime:"2023-03-16 15:05:54",
ActiveCount:0,
PoolingCount:0,
CreateCount:0,
DestroyCount:0,
CloseCount:0,
ConnectCount:0,
Connections:[
]
}
|
如果有多个 bean 要被 Spring 管理,直接在配置类中多些几个方法,方法上添加 @Bean 注解即可。
1.7.2 引入外部配置类
如果把所有的第三方 bean 都配置到 Spring 的配置类 SpringConfig 中,虽然可以,但是不利于代码阅读和分类管理,所有我们就想能不能按照类别将这些bean配置到不同的配置类中?
对于数据源的bean,我们新建一个 JdbcConfig 配置类,并把数据源配置到该类下。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| public class JdbcConfig {
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource() {
DruidDataSource ds = new DruidDataSource();
ds.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
ds.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring_db");
ds.setUsername("root");
ds.setPassword("root");
return ds;
}
}
|
现在的问题是,这个配置类如何能被 Spring 配置类加载到,并创建 DataSource 对象在 IOC 容器中?
针对这个问题,有两个解决方案:
- 使用包扫描引入
- 使用
@Import 引入
使用包扫描引入
a. 在Spring的配置类上添加包扫描
1
2
3
4
| @Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.muyoukule.Config")
public class SpringConfig {
}
|
b. 在 JdbcConfig 上添加配置注解
JdbcConfig 类要放入到 com.muyoukule.Config 包下,需要被 Spring 的配置类扫描到即可
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| @Configuration
public class JdbcConfig {
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource() {
DruidDataSource ds = new DruidDataSource();
ds.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
ds.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring_db");
ds.setUsername("root");
ds.setPassword("root");
return ds;
}
}
|
c. 运行程序
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| {
CreateTime:"2023-03-16 15:22:46",
ActiveCount:0,
PoolingCount:0,
CreateCount:0,
DestroyCount:0,
CloseCount:0,
ConnectCount:0,
Connections:[
]
}
|
这种方式虽然能够扫描到,但是不能很快的知晓都引入了哪些配置类,所有这种方式不推荐使用。
使用 @Import 引入
方案一实现起来有点小复杂,Spring 早就想到了这一点,于是又给我们提供了第二种方案。
这种方案可以不用加 @Configuration 注解,但是必须在Spring配置类上使用 @Import 注解手动引入需要加载的配置类
a. 去除JdbcConfig类上的注解
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| public class JdbcConfig {
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource() {
DruidDataSource ds = new DruidDataSource();
ds.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
ds.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring_db");
ds.setUsername("root");
ds.setPassword("root");
return ds;
}
}
|
b. 在Spring配置类中引入
1
2
3
4
5
| @Configuration
@Import({JdbcConfig.class})
public class SpringConfig {
}
|
注意:
c. 运行程序
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| {
CreateTime:"2024-03-16 15:27:17",
ActiveCount:0,
PoolingCount:0,
CreateCount:0,
DestroyCount:0,
CloseCount:0,
ConnectCount:0,
Connections:[
]
}
|
1.7.3 注解开发实现为第三方bean注入资源
在使用 @Bean 创建 bean 对象的时候,如果方法在创建的过程中需要其他资源该怎么办?
这些资源会有两大类,分别是 简单数据类型 和 引用数据类型 。
1.7.3.1 简单数据类型
对于下面代码关于数据库的四要素不应该写死在代码中,应该是从properties配置文件中读取。如何来优化下面的代码?
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| public class JdbcConfig {
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource() {
DruidDataSource ds = new DruidDataSource();
ds.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
ds.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring_db");
ds.setUsername("root");
ds.setPassword("root");
return ds;
}
}
|
注入简单数据类型
a. 类中提供四个属性
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| public class JdbcConfig {
private String driver;
private String url;
private String userName;
private String password;
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource() {
DruidDataSource ds = new DruidDataSource();
ds.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
ds.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring_db");
ds.setUsername("root");
ds.setPassword("root");
return ds;
}
}
|
b. 使用 @Value 注解引入值
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| public class JdbcConfig {
@Value("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver")
private String driver;
@Value("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring_db")
private String url;
@Value("root")
private String userName;
@Value("password")
private String password;
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource() {
DruidDataSource ds = new DruidDataSource();
ds.setDriverClassName(driver);
ds.setUrl(url);
ds.setUsername(userName);
ds.setPassword(password);
return ds;
}
}
|
扩展
现在的数据库连接四要素还是写在代码中,需要做的是将这些内容提取到jdbc.properties配置文件,该如何实现?
resources目录下添加 jdbc.properties
配置文件中提供四个键值对分别是数据库的四要素
使用 @PropertySource 加载 jdbc.properties 配置文件
修改 @Value 注解属性的值,将其修改为${key},key 就是键值对中的键的值
1.7.3.2 引用数据类型
假设在构建 DataSource 对象的时候,需要用到 BookDao 对象,该如何把 BookDao 对象注入进方法内让其使用呢?
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| public class JdbcConfig {
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource() {
DruidDataSource ds = new DruidDataSource();
ds.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
ds.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring_db");
ds.setUsername("root");
ds.setPassword("root");
return ds;
}
}
|
注入引用数据类型
a. 在 SpringConfig 中扫描 BookDao
扫描的目的是让 Spring 能管理到 BookDao ,也就是说要让 IOC 容器中有一个 bookDao 对象
1
2
3
4
5
| @Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.muyoukule.Dao")
@Import({JdbcConfig.class})
public class SpringConfig {
}
|
b. 在 JdbcConfig 类的方法上添加参数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| public class JdbcConfig {
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource(BookDao bookDao) {
System.out.println(bookDao);
DruidDataSource ds = new DruidDataSource();
ds.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
ds.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring_db");
ds.setUsername("root");
ds.setPassword("root");
return ds;
}
}
|
引用类型注入只需要为bean定义方法设置形参即可,容器会根据类型 byType 自动装配对象。
c. 运行程序
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| com.muyoukule.Dao.BookDaoImpl@6572421
{
CreateTime:"2023-03-16 15:38:04",
ActiveCount:0,
PoolingCount:0,
CreateCount:0,
DestroyCount:0,
CloseCount:0,
ConnectCount:0,
Connections:[
]
}
|
2. 面向切面编程AOP
IoC使软件组件松耦合。AOP让你能够捕捉系统中经常使用的功能,把它转化成组件。
AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming):面向切面编程,面向方面编程。(AOP是一种编程技术)
AOP 是对OOP的补充延伸。
AOP 底层使用的就是动态代理来实现的。
Spring 的 AOP 使用的动态代理是:JDK 动态代理 + CGLIB 动态代理技术。Spring 在这两种动态代理中灵活切换,如果是代理接口,会默认使用 JDK 动态代理,如果要代理某个类,这个类没有实现接口,就会切换使用 CGLIB。当然,你也可以强制通过一些配置让 Spring 只使用 CGLIB。
2.1 AOP介绍
一般一个系统当中都会有一些系统服务,例如:日志、事务管理、安全等。这些系统服务被称为:交叉业务
这些交叉业务几乎是通用的,不管你是做银行账户转账,还是删除用户数据。日志、事务管理、安全,这些都是需要做的。
如果在每一个业务处理过程当中,都掺杂这些交叉业务代码进去的话,存在两方面问题:
- 交叉业务代码在多个业务流程中反复出现,显然这个交叉业务代码没有得到复用。并且修改这些交叉业务代码的话,需要修改多处。
- 程序员无法专注核心业务代码的编写,在编写核心业务代码的同时还需要处理这些交叉业务。
使用AOP可以很轻松的解决以上问题。
请看下图,可以帮助你快速理解AOP的思想:
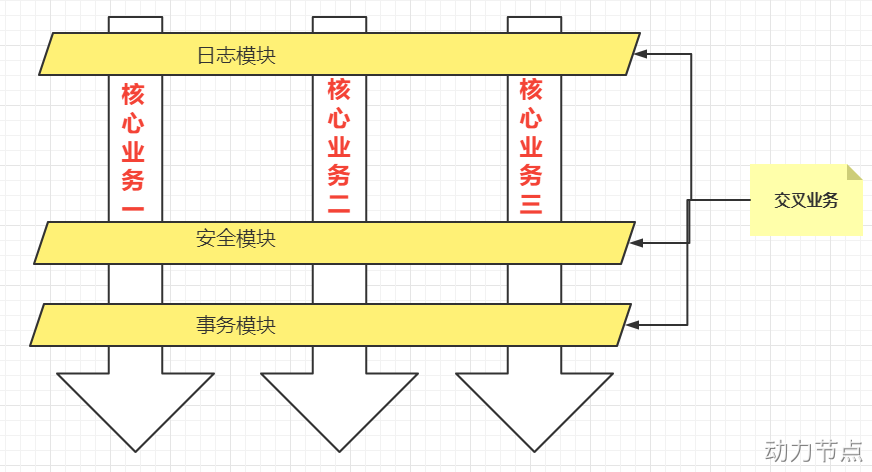
用一句话总结AOP:将与核心业务无关的代码独立的抽取出来,形成一个独立的组件,然后以横向交叉的方式应用到业务流程当中的过程被称为AOP。
AOP的优点:
- 代码复用性增强。
- 代码易维护。
- 使开发者更关注业务逻辑。
2.2 AOP的七大术语
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| public class UserService {
public void do1() {
System.out.println("do 1");
}
public void do2() {
System.out.println("do 2");
}
public void do3() {
System.out.println("do 3");
}
public void do4() {
System.out.println("do 4");
}
public void do5() {
System.out.println("do 5");
}
public void service() {
do1();
do2();
do3();
do5();
}
}
|
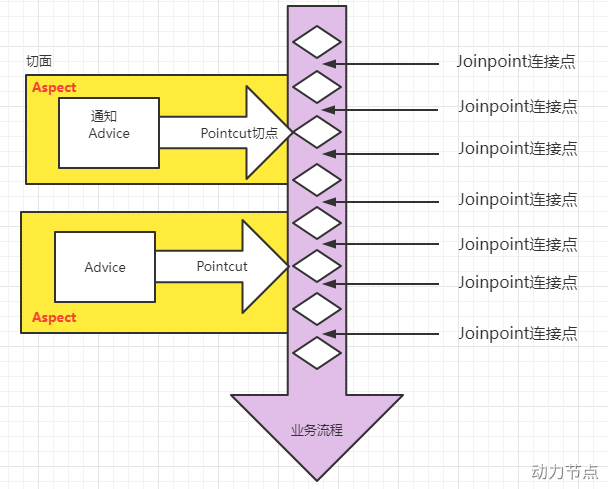
连接点 Joinpoint
- 在程序的整个执行流程中,可以织入切面的位置。方法的执行前后,异常抛出之后等位置。
切点 Pointcut
- 在程序执行流程中,真正织入切面的方法。(一个切点对应多个连接点)
通知 Advice
通知又叫增强,就是具体你要织入的代码。
通知包括:
切面 Aspect
织入 Weaving
代理对象 Proxy
目标对象 Target
通过下图,大家可以很好的理解AOP的相关术语:
2.3 切点表达式
切点表达式用来定义通知(Advice)往哪些方法上切入。
切入点表达式语法格式:
1
| execution([访问控制权限修饰符] 返回值类型 [全限定类名]方法名(形式参数列表) [异常])
|
访问控制权限修饰符:
- 可选项。
- 没写,就是4个权限都包括。
- 写 public 就表示只包括公开的方法。
返回值类型:
全限定类名:
- 可选项。
- 两个点“..”代表当前包以及子包下的所有类。
- 省略时表示所有的类。
方法名:
- 必填项。
- *表示所有方法。
- set*表示所有的set方法。
形式参数列表:
异常:
理解以下的切点表达式:
Service包下所有的类中以 delete 开始的所有方法
1
| execution(public * com.muyoukule.Service.*.delete*(..))
|
Mall包下所有的类的所有的方法
1
| execution(* com.muyoukule.Mall..*(..))
|
所有类的所有方法
2.4 使用Spring的AOP
Spring对AOP的实现包括以下3种方式:
- 第一种方式:Spring框架结合AspectJ框架实现的AOP,基于注解方式。
- 第二种方式:Spring框架结合AspectJ框架实现的AOP,基于XML方式。
- 第三种方式:Spring框架自己实现的AOP,基于XML配置方式。
实际开发中,都是 Spring+AspectJ 来实现 AOP。所以我们重点学习第一种和第二种方式。
什么是AspectJ?(Eclipse组织的一个支持AOP的框架。AspectJ框架是独立于Spring框架之外的一个框架,Spring框架用了AspectJ)
环境准备
a. 使用Spring+AspectJ的AOP需要引入的依赖,由于在spring-context中已经包含了spring aop依赖,所以只需引入以下依赖:

1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| <dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.3.27</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aspects</artifactId>
<version>5.3.27</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.13.2</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
|
b. Spring配置文件 spring.xml 中添加 context 命名空间和 aop 命名空间
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
</beans>
|
2.4.1 基于AspectJ的AOP注解式开发
实现步骤
a. 定义目标类以及目标方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
public class OrderService {
public void generate() {
System.out.println("订单已生成!");
}
}
|
b. 定义切面类
1
2
3
4
|
@Aspect
public class MyAspect {
}
|
c. 目标类和切面类都纳入spring bean管理
d. 在spring配置文件中添加组建扫描
1
2
|
<context:component-scan base-package="com.muyoukule.Service,com.muyoukule.Aspect"/>
|
e. 在切面类中添加通知
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
@Aspect
@Component
public class MyAspect {
public void advice() {
System.out.println("我是一个通知");
}
}
|
f. 在通知上添加切点表达式(通知+切点=切面)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
@Aspect
@Component
public class MyAspect {
@Before("execution(* com.muyoukule.Service.OrderService.*(..))")
public void advice() {
System.out.println("我是一个通知");
}
}
|
PS:注解 @Before 表示前置通知。
g. 在 spring 配置文件中启用自动代理
1
2
3
4
|
<context:component-scan base-package="com.muyoukule.Service"/>
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy proxy-target-class="true"/>
|
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy proxy-target-class="true"/> 开启自动代理之后,凡是带有 @Aspect 注解的 bean 都会生成代理对象。
proxy-target-class="true" 表示采用cglib动态代理。
proxy-target-class="false" 表示采用 jdk 动态代理。默认值是 false。即使写成 false,当没有接口的时候,也会自动选择 cglib 生成代理类。
h. 测试程序
1
2
3
4
5
6
| @Test
public void testAOP() {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
OrderService orderService = applicationContext.getBean("orderService", OrderService.class);
orderService.generate();
}
|
i. 运行结果:
通知类型
通知类型包括:
- 前置通知:
@Before 目标方法执行之前的通知。
- 后置通知:
@AfterReturning 目标方法执行之后的通知。
- 环绕通知:
@Around 目标方法之前添加通知,同时目标方法执行之后添加通知。
- 异常通知:
@AfterThrowing 发生异常之后执行的通知。
- 最终通知:
@After 放在 finally 语句块中的通知。
接下来,改写程序来测试这几个通知的执行顺序
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
|
@Component
@Aspect
public class MyAspect {
@Around("execution(* com.muyoukule.Service.OrderService.*(..))")
public void aroundAdvice(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("环绕通知开始");
proceedingJoinPoint.proceed();
System.out.println("环绕通知结束");
}
@Before("execution(* com.muyoukule.Service.OrderService.*(..))")
public void beforeAdvice() {
System.out.println("前置通知");
}
@AfterReturning("execution(* com.muyoukule.Service.OrderService.*(..))")
public void afterReturningAdvice() {
System.out.println("后置通知");
}
@AfterThrowing("execution(* com.muyoukule.Service.OrderService.*(..))")
public void afterThrowingAdvice() {
System.out.println("异常通知");
}
@After("execution(* com.muyoukule.Service.OrderService.*(..))")
public void afterAdvice() {
System.out.println("最终通知");
}
}
|
运行测试,结果
1
2
3
4
5
6
| 环绕通知开始
前置通知
订单已生成!
后置通知
最终通知
环绕通知结束
|
结果中没有异常通知,这是因为目标程序执行过程中没有发生异常。
尝试让目标方法发生异常
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
@Service
public class OrderService {
public void generate() {
System.out.println("订单已生成!");
if (1 == 1) {
throw new RuntimeException("模拟异常发生");
}
}
}
|
再次执行测试程序
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| 环绕通知开始
前置通知
订单已生成!
异常通知
最终通知
java.lang.RuntimeException: 模拟异常发生
// --snip--
|
通过测试得知,当发生异常之后,最终通知也会执行,因为最终通知 @After 会出现在 finally 语句块中。出现异常之后,后置通知和环绕通知的结束部分不会执行。
切面的先后顺序
我们知道,业务流程当中不一定只有一个切面,可能有的切面控制事务,有的记录日志,有的进行安全控制,如果多个切面的话,顺序如何控制:可以使用 @Order 注解来标识切面类,为 @Order 注解的 value 指定一个整数型的数字,数字越小,优先级越高。
a. 再定义一个切面类,并设置优先级
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
| @Aspect
@Component
@Order(1)
public class YourAspect {
@Around("execution(* com.muyoukule.Service.OrderService.*(..))")
public void aroundAdvice(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("YourAspect环绕通知开始");
proceedingJoinPoint.proceed();
System.out.println("YourAspect环绕通知结束");
}
@Before("execution(* com.muyoukule.Service.OrderService.*(..))")
public void beforeAdvice() {
System.out.println("YourAspect前置通知");
}
@AfterReturning("execution(* com.muyoukule.Service.OrderService.*(..))")
public void afterReturningAdvice() {
System.out.println("YourAspect后置通知");
}
@AfterThrowing("execution(* com.muyoukule.Service.OrderService.*(..))")
public void afterThrowingAdvice() {
System.out.println("YourAspect异常通知");
}
@After("execution(* com.muyoukule.Service.OrderService.*(..))")
public void afterAdvice() {
System.out.println("YourAspect最终通知");
}
}
|
b. 设置切面类 MyAspect 的优先级
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
@Component
@Aspect
@Order(2)
public class MyAspect {
}
|
c. 执行测试程序
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| YourAspect环绕通知开始
YourAspect前置通知
环绕通知开始
前置通知
订单已生成!
后置通知
最终通知
环绕通知结束
YourAspect后置通知
YourAspect最终通知
YourAspect环绕通知结束
|
通过修改 @Order 注解的整数值来切换顺序,执行测试程序:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| 环绕通知开始
前置通知
YourAspect环绕通知开始
YourAspect前置通知
订单已生成!
YourAspect后置通知
YourAspect最终通知
YourAspect环绕通知结束
后置通知
最终通知
环绕通知结束
|
优化使用切点表达式
观看刚才代码中的切点表达式,缺点是:
- 切点表达式重复写了多次,没有得到复用。
- 如果要修改切点表达式,需要修改多处,难维护。
可以这样做:将切点表达式单独的定义出来,在需要的位置引入即可。如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
@Component
@Aspect
@Order(2)
public class MyAspect {
@Pointcut("execution(* com.muyoukule.Service..*(..))")
public void pointcut() {
}
@Around("pointcut()")
public void aroundAdvice(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("环绕通知开始");
proceedingJoinPoint.proceed();
System.out.println("环绕通知结束");
}
@Before("pointcut()")
public void beforeAdvice() {
System.out.println("前置通知");
}
}
|
使用 @Pointcut 注解来定义独立的切点表达式。注意这个 @Pointcut 注解标注的方法随意,只是起到一个能够让 @Pointcut 注解编写的位置。
运行测试
1
2
3
4
5
6
| 环绕通知开始
前置通知
订单已生成!
后置通知
最终通知
环绕通知结束
|
全注解式开发AOP
就是编写一个类,在这个类上面使用大量注解来代替 spring 的配置文件,spring 配置文件消失了,如下:
1
2
3
4
5
| @Configuration
@ComponentScan({"com.muyoukule.Service", "com.muyoukule.Aspect"})
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy(proxyTargetClass = true)
public class SpringConfig {
}
|
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy(proxyTargetClass = true) 或者 @EnableAspectJAutoProxy 开启注解格式AOP功能。proxyTargetClass = true 表示采用 cglib 动态代理。
测试程序也变化了
1
2
3
4
5
6
| @Test
public void testAOPWithAllAnnotation() {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
OrderService orderService = applicationContext.getBean("orderService", OrderService.class);
orderService.generate();
}
|
2.4.2 基于XML配置方式的AOP(了解)
a. 编写目标类(不添加注解)
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
public class VipService {
public void add() {
System.out.println("保存vip信息...");
}
}
|
b. 编写切面类,并且编写通知(不添加 @Component 注解)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
public class TimerAspect {
public void time(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) throws Throwable {
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
proceedingJoinPoint.proceed();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("耗时" + (end - begin) + "毫秒");
}
}
|
c. 编写 spring.xml 配置文件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<bean id="vipService" class="com.muyoukule.Service.VipService"/>
<bean id="timerAspect" class="com.muyoukule.Aspect.TimerAspect"/>
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut id="p" expression="execution(* com.muyoukule.Service.VipService.*(..))"/>
<aop:aspect ref="timerAspect">
<aop:around method="time" pointcut-ref="p"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
</beans>
|
d. 测试程序
1
2
3
4
5
6
| @Test
public void testAOPXml() {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
VipService vipService = applicationContext.getBean("vipService", VipService.class);
vipService.add();
}
|
e. 结果
2.5 AOP的实际案例:事务处理
项目中的事务控制是在所难免的。在一个业务流程当中,可能需要多条 DML 语句共同完成,为了保证数据的安全,这多条 DML 语句要么同时成功,要么同时失败。这就需要添加事务控制的代码。例如以下伪代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
| class 业务类1{
public void 业务方法1(){
try{
startTransaction();
step1();
step2();
step3();
....
commitTransaction();
}catch(Exception e){
rollbackTransaction();
}
}
public void 业务方法2(){
try{
startTransaction();
step1();
step2();
step3();
....
commitTransaction();
}catch(Exception e){
rollbackTransaction();
}
}
public void 业务方法3(){
try{
startTransaction();
step1();
step2();
step3();
....
commitTransaction();
}catch(Exception e){
rollbackTransaction();
}
}
}
class 业务类2{
public void 业务方法1(){
try{
startTransaction();
step1();
step2();
step3();
....
commitTransaction();
}catch(Exception e){
rollbackTransaction();
}
}
public void 业务方法2(){
try{
startTransaction();
step1();
step2();
step3();
....
commitTransaction();
}catch(Exception e){
rollbackTransaction();
}
}
public void 业务方法3(){
try{
startTransaction();
step1();
step2();
step3();
....
commitTransaction();
}catch(Exception e){
rollbackTransaction();
}
}
}
|
可以看到,这些业务类中的每一个业务方法都是需要控制事务的,而控制事务的代码又是固定的格式,都是:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| try{
startTransaction();
commitTransaction();
}catch(Exception e){
rollbackTransaction();
}
|
这个控制事务的代码就是和业务逻辑没有关系的 “交叉业务” 。以上伪代码当中可以看到这些交叉业务的代码没有得到复用,并且如果这些交叉业务代码需要修改,那必然需要修改多处,难维护,怎么解决?可以采用 AOP 思想解决。可以把以上控制事务的代码作为环绕通知,切入到目标类的方法当中。
a. 有两个业务类,如下
银行账户的业务类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| @Service
public class AccountService {
public void transfer() {
System.out.println("正在进行银行账户转账...");
}
public void withdraw() {
System.out.println("正在进行取款操作...");
}
}
|
订单业务类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| @Service
public class OrderService {
public void generate() {
System.out.println("正在生成订单...");
}
public void cancel() {
System.out.println("正在取消订单...");
}
}
|
注意,以上两个业务类已经纳入spring bean的管理,因为都添加了 @Service 注解。
给以上两个业务类的4个方法添加事务控制代码,使用 AOP 来完成:
b. 事务切面类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| @Aspect
@Component
public class TransactionAspect {
@Around("execution(* com.muyoukule.Service..*(..))")
public void aroundAdvice(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) {
try {
System.out.println("开启事务");
proceedingJoinPoint.proceed();
System.out.println("提交事务");
} catch (Throwable e) {
System.out.println("回滚事务");
}
}
}
|
c. 编写配置类
1
2
3
4
5
| @Configuration
@ComponentScan({"com.muyoukule.Service", "com.muyoukule.Aspect"})
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy(proxyTargetClass = true)
public class SpringConfig {
}
|
这个事务控制代码只需要写一次就行了,并且修改起来也没有成本。
d. 编写测试程序:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| @Test
public void testTransaction() {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
OrderService orderService = applicationContext.getBean("orderService", OrderService.class);
AccountService accountService = applicationContext.getBean("accountService", AccountService.class);
orderService.generate();
orderService.cancel();
accountService.transfer();
accountService.withdraw();
}
|
e. 运行结果
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| 开启事务
正在生成订单...
提交事务
开启事务
正在取消订单...
提交事务
开启事务
正在进行银行账户转账...
提交事务
开启事务
正在进行取款操作...
提交事务
|
2.6 AOP的实际案例:安全日志
需求是这样的:项目开发结束了,已经上线了。运行正常。客户提出了新的需求:凡事在系统中进行修改操作的,删除操作的,新增操作的,都要把这个人记录下来。因为这几个操作是属于危险行为。例如有业务类和业务方法:
用户业务类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| @Service
public class UserService {
public void getUser() {
System.out.println("获取用户信息...");
}
public void saveUser() {
System.out.println("保存用户...");
}
public void deleteUser() {
System.out.println("删除用户...");
}
public void modifyUser() {
System.out.println("修改用户...");
}
}
|
商品业务类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
@Service
public class ProductService {
public void getProduct() {
System.out.println("获取商品信息....");
}
public void saveProduct() {
System.out.println("保存商品....");
}
public void deleteProduct() {
System.out.println("删除商品....");
}
public void modifyProduct() {
System.out.println("修改商品....");
}
}
|
接下来我们使用aop来解决上面的需求:编写一个负责安全的切面类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| @Component
@Aspect
public class SecurityAspect {
@Pointcut("execution(* com.muyoukule.Service..save*(..))")
public void savePointcut() {
}
@Pointcut("execution(* com.muyoukule.Service..delete*(..))")
public void deletePointcut() {
}
@Pointcut("execution(* com.muyoukule.Service..modify*(..))")
public void modifyPointcut() {
}
@Before("savePointcut() || deletePointcut() || modifyPointcut()")
public void beforeAdivce(JoinPoint joinpoint) {
System.out.println("XXX操作员正在操作" + joinpoint.getSignature().getName() + "方法");
}
}
|
测试程序
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| @Test
public void testSecurity() {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
UserService userService = applicationContext.getBean("userService", UserService.class);
ProductService productService = applicationContext.getBean("productService", ProductService.class);
userService.getUser();
userService.saveUser();
userService.deleteUser();
userService.modifyUser();
productService.getProduct();
productService.saveProduct();
productService.deleteProduct();
productService.modifyProduct();
}
|
编写配置类
1
2
3
4
5
| @Configuration
@ComponentScan({"com.muyoukule.Service", "com.muyoukule.Aspect"})
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy(proxyTargetClass = true)
public class SpringConfig {
}
|
结果
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| 获取用户信息
XXX操作员正在操作saveUser方法
保存用户
XXX操作员正在操作deleteUser方法
删除用户
XXX操作员正在操作modifyUser方法
修改用户
获取商品信息
XXX操作员正在操作saveProduct方法
保存商品
XXX操作员正在操作deleteProduct方法
删除商品
XXX操作员正在操作modifyProduct方法
修改商品
|
3. Spring对事务的支持
3.1 事务概述
3.2 Spring事务案例
数据层有事务我们可以理解,为什么业务层也需要处理事务呢?
举个简单的例子:
- 转账业务会有两次数据层的调用,一次是加钱一次是减钱。
- 把事务放在数据层,加钱和减钱就有两个事务。
- 没办法保证加钱和减钱同时成功或者同时失败。
- 这个时候就需要将事务放在业务层进行处理。
Spring 为了管理事务,提供了一个平台事务管理器 PlatformTransactionManager
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| public interface PlatformTransactionManager extends TransactionManager {
TransactionStatus getTransaction(@Nullable TransactionDefinition definition) throws TransactionException;
void commit(TransactionStatus status) throws TransactionException;
void rollback(TransactionStatus status) throws TransactionException;
}
|
commit 是用来提交事务,rollback 是用来回滚事务。
PlatformTransactionManager 只是一个接口,Spring还为其提供了一个具体的实现:DataSourceTransactionManager
从名称上可以看出,我们只需要给它一个 DataSource 对象,它就可以帮你去在业务层管理事务。其内部采用的是 JDBC 的事务。所以说如果你持久层采用的是JDBC相关的技术,就可以采用这个事务管理器来管理你的事务。而 Mybatis 内部采用的就是 JDBC 的事务,所以后期我们 Spring 整合 Mybatis 就采用的这个 DataSourceTransactionManager 事务管理器。
小Tips😀:关于整合的知识可以在本站搜索查看 Spring整合 学习。
3.2.1 转账案例-需求分析
接下来通过一个案例来学习下Spring是如何来管理事务的。
先来分析下需求:
需求: 实现任意两个账户间转账操作
需求微缩: A账户减钱,B账户加钱
为了实现上述的业务需求,我们可以按照下面步骤来实现下:
- 数据层提供基础操作,指定账户减钱(outMoney),指定账户加钱(inMoney)
- 业务层提供转账操作(transfer),调用减钱与加钱的操作
- 提供2个账号和操作金额执行转账操作
- 基于 Spring 整合 MyBatis 环境搭建上述操作
3.2.2 转账案例-环境搭建
a. 准备数据库表
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| create database spring_db character set utf8;
use spring_db;
create table tbl_account(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(35),
money double
);
insert into tbl_account values(1,'Tom',1000);
insert into tbl_account values(2,'Jerry',1000);
|
b. 创建项目导入jar包,项目的 pom.xml 添加相关依赖
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
| <dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.3.27</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.1.16</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.5.6</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.31</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>5.3.27</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring</artifactId>
<version>1.3.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
<version>5.3.27</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.18.24</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
|
c. 根据表创建模型类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| @Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class Account implements Serializable {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Double money;
}
|
d. 创建 Dao 接口
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| public interface AccountDao {
@Update("update tbl_account set money = money + #{money} where name = #{name}")
void inMoney(@Param("name") String name, @Param("money") Double money);
@Update("update tbl_account set money = money - #{money} where name = #{name}")
void outMoney(@Param("name") String name, @Param("money") Double money);
}
|
e. 创建 Service 接口和实现类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| public interface AccountService {
public void transfer(String out,String in ,Double money) ;
}
@Service
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
@Autowired
private AccountDao accountDao;
public void transfer(String out,String in ,Double money) {
accountDao.outMoney(out,money);
accountDao.inMoney(in,money);
}
}
|
f. 添加 jdbc.properties 文件
1
2
3
4
| jdbc.driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring_db?useSSL=false
jdbc.username=root
jdbc.password=root
|
g. 创建 JdbcConfig 配置类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| public class JdbcConfig {
@Value("${jdbc.driver}")
private String driver;
@Value("${jdbc.url}")
private String url;
@Value("${jdbc.username}")
private String userName;
@Value("${jdbc.password}")
private String password;
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource(){
DruidDataSource ds = new DruidDataSource();
ds.setDriverClassName(driver);
ds.setUrl(url);
ds.setUsername(userName);
ds.setPassword(password);
return ds;
}
}
|
h. 创建 MybatisConfig 配置类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| public class MybatisConfig {
@Bean
public SqlSessionFactoryBean sqlSessionFactory(DataSource dataSource) {
SqlSessionFactoryBean ssfb = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
ssfb.setTypeAliasesPackage("com.muyoukule.Entity");
ssfb.setDataSource(dataSource);
return ssfb;
}
@Bean
public MapperScannerConfigurer mapperScannerConfigurer() {
MapperScannerConfigurer msc = new MapperScannerConfigurer();
msc.setBasePackage("com.muyoukule.Dao");
return msc;
}
}
|
i. 创建SpringConfig 配置类
1
2
3
4
5
6
| @Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.muyoukule")
@PropertySource("classpath:jdbc.properties")
@Import({JdbcConfig.class, MybatisConfig.class})
public class SpringConfig {
}
|
j. 编写测试类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| @RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(classes = SpringConfig.class)
public class AccountServiceTest {
@Autowired
private AccountService accountService;
@Test
public void testTransfer() throws IOException {
accountService.transfer("Tom","Jerry",100D);
}
}
|
3.2.3 事务管理
上述环境,运行单元测试类,会执行转账操作,Tom的账户会减少100,Jerry的账户会加100。
这是正常情况下的运行结果,但是如果在转账的过程中出现了异常,如:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| @Service
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
@Autowired
private AccountDao accountDao;
public void transfer(String out,String in ,Double money) {
accountDao.outMoney(out,money);
int i = 1/0;
accountDao.inMoney(in,money);
}
}
|
这个时候就模拟了转账过程中出现异常的情况,正确的操作应该是转账出问题了,Tom 应该还是900,Jerry 应该还是1100,但是真正运行后会发现,并没有像我们想象的那样,Tom 账户为800而 Jerry 还是1100,100块钱凭空消失了,银行乐疯了。如果把转账换个顺序,银行就该哭了。
不管哪种情况,都是不允许出现的,对刚才的结果我们做一个分析:
程序正常执行时,账户金额A减B加,没有问题
程序出现异常后,转账失败,但是异常之前操作成功,异常之后操作失败,整体业务失败
当程序出问题后,我们需要让事务进行回滚,而且这个事务应该是加在业务层上,而 Spring 的事务管理就是用来解决这类问题的。
Spring 事务管理具体的实现步骤
a. 在需要被事务管理的方法上添加注解
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| public interface AccountService {
public void transfer(String out,String in ,Double money) ;
}
@Service
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
@Autowired
private AccountDao accountDao;
@Transactional
public void transfer(String out, String in, Double money) {
accountDao.outMoney(out, money);
int i = 1 / 0;
accountDao.inMoney(in, money);
}
}
|
注意:
@Transactional 可以写在接口类上、接口方法上、实现类上和实现类方法上
- 写在接口类上,该接口的所有实现类的所有方法都会有事务
- 写在接口方法上,该接口的所有实现类的该方法都会有事务
- 写在实现类上,该类中的所有方法都会有事务
- 写在实现类方法上,该方法上有事务
- 建议写在实现类或实现类的方法上
b. 在 JdbcConfig 类中配置事务管理器
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| public class JdbcConfig {
@Bean
public PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager(DataSource dataSource){
DataSourceTransactionManager transactionManager = new DataSourceTransactionManager();
transactionManager.setDataSource(dataSource);
return transactionManager;
}
}
|
注意:事务管理器要根据使用技术进行选择,Mybatis 框架使用的是 JDBC 事务,可以直接使用 DataSourceTransactionManager
c. 开启事务注解
在 SpringConfig 的配置类中开启
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| @Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.muyoukule")
@PropertySource("classpath:jdbc.properties")
@Import({JdbcConfig.class, MybatisConfig.class})
@EnableTransactionManagement
public class SpringConfig {
}
|
d. 运行测试类
会发现在转换的业务出现错误后,事务就可以控制回顾,保证数据的正确性。
3.3 Spring事务角色
这节中我们重点要理解两个概念,分别是 事务管理员 和 事务协调员 。
- 未开启Spring事务之前:
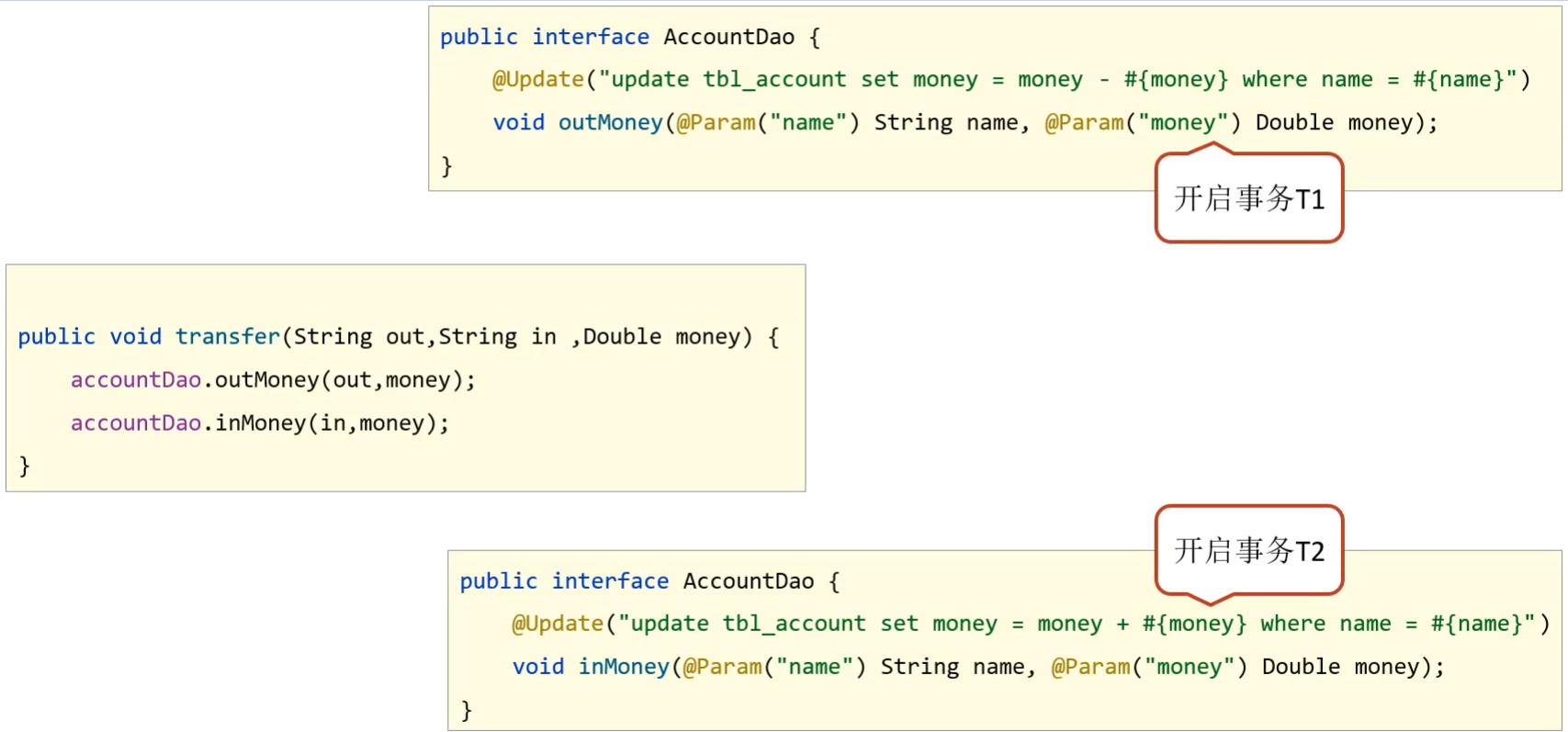
- AccountDao 的 outMoney 因为是修改操作,会开启一个事务T1
- AccountDao 的 inMoney 因为是修改操作,会开启一个事务T2
- AccountService 的 transfer 没有事务,
- 运行过程中如果没有抛出异常,则T1和T2都正常提交,数据正确
- 如果在两个方法中间抛出异常,T1因为执行成功提交事务,T2因为抛异常不会被执行
- 就会导致数据出现错误
- 开启Spring的事务管理后
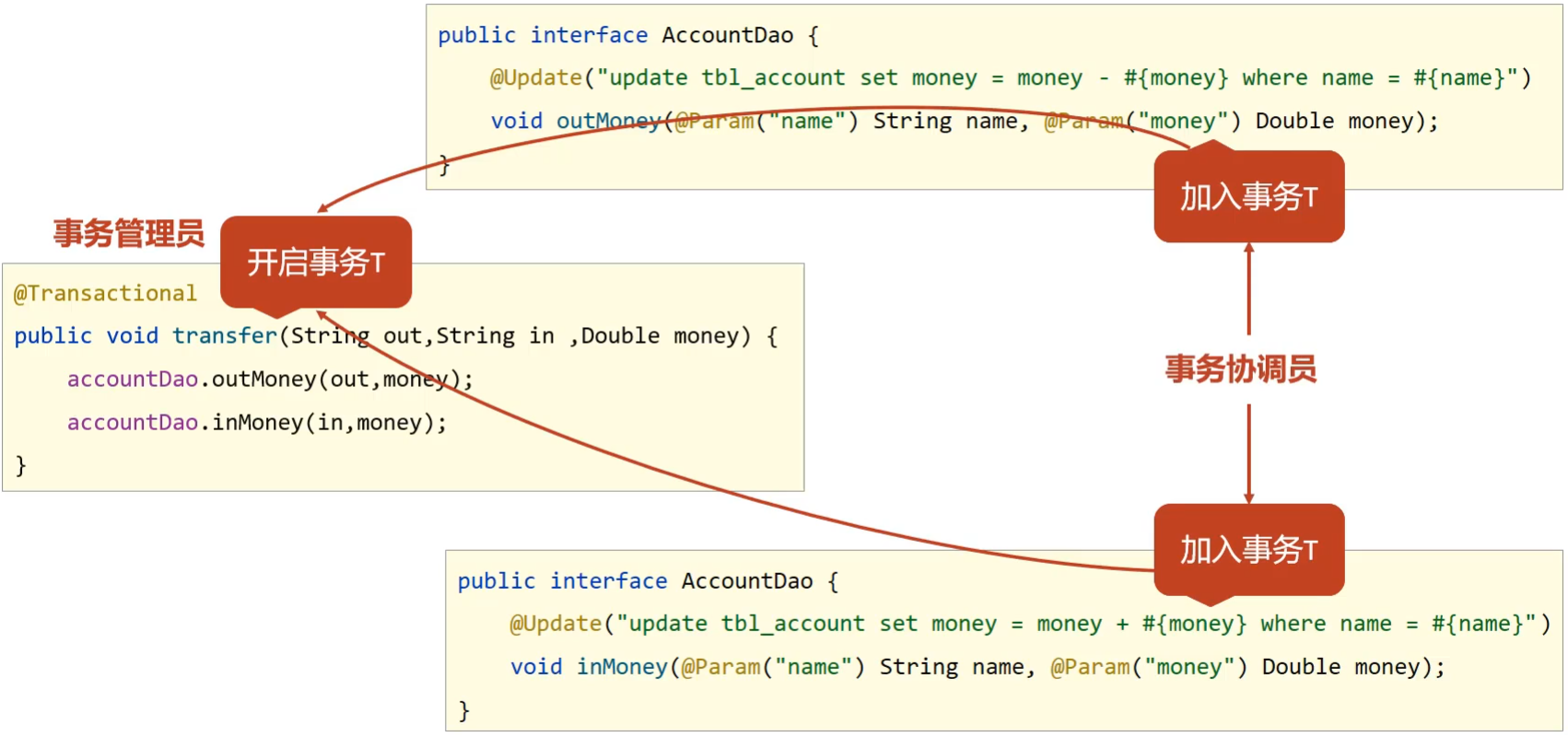
- transfer上添加了
@Transactional 注解,在该方法上就会有一个事务T
- AccountDao的 outMoney 方法的事务T1加入到 transfer 的事务T中
- AccountDao的 inMoney 方法的事务T2加入到 transfer 的事务T中
- 这样就保证他们在同一个事务中,当业务层中出现异常,整个事务就会回滚,保证数据的准确性。
通过上面例子的分析,我们就可以得到如下概念:
- 事务管理员:发起事务方,在Spring中通常指代业务层开启事务的方法
- 事务协调员:加入事务方,在Spring中通常指代数据层方法,也可以是业务层方法
注意:
目前的事务管理是基于 DataSourceTransactionManager 和 SqlSessionFactoryBean 使用的是同一个数据源。
3.4 Spring事务属性
上一节我们介绍了两个概念,事务的管理员和事务的协同员,对于这两个概念具体做什么的,我们待会通过案例来使用下。除了这两个概念,还有就是事务的其他相关配置都有哪些,就是我们接下来要学习的内容。
在这一节中,我们主要学习三部分内容 事务配置 、 转账业务追加日志 、 事务传播行为。
3.4.1 事务配置

上面这些属性都可以在 @Transactional 注解的参数上进行设置:
readOnly:true 只读事务,false 读写事务,增删改要设为 false,查询设为 true。
timeout:设置超时时间单位秒,在多长时间之内事务没有提交成功就自动回滚,-1表示不设置超时时间。
rollbackFor:当出现指定异常进行事务回滚
noRollbackFor:当出现指定异常不进行事务回滚
思考:出现异常事务会自动回滚,这个是我们之前就已经知道的
noRollbackFor 是设定对于指定的异常不回滚,这个好理解
rollbackFor 是指定回滚异常,对于异常事务不应该都回滚么,为什么还要指定?
出现这个问题的原因是,Spring的事务只会对 Error 异常 和 RuntimeException 异常及其子类进行事务回顾,其他的异常类型是不会回滚的,对应 IOException 不符合上述条件所以不回滚
rollbackForClassName 等同于 rollbackFor,只不过属性为异常的类全名字符串
noRollbackForClassName 等同于 noRollbackFor,只不过属性为异常的类全名字符串
isolation 设置事务的隔离级别
- DEFAULT:默认隔离级别, 会采用数据库的隔离级别
- READ_UNCOMMITTED:读未提交
- READ_COMMITTED:读已提交
- REPEATABLE_READ:重复读取
- SERIALIZABLE:串行化
介绍完上述属性后,还有最后一个事务的传播行为,为了讲解该属性的设置,我们需要完成下面的案例。
3.4.2 转账业务追加日志案例
3.4.2.1 需求分析
在前面的转案例的基础上添加新的需求,完成转账后记录日志。
- 需求:实现任意两个账户间转账操作,并对每次转账操作在数据库进行留痕
- 需求微缩:A账户减钱,B账户加钱,数据库记录日志
基于上述的业务需求,我们来分析下该如何实现:
基于转账操作案例添加日志模块,实现数据库中记录日志
业务层转账操作(transfer),调用减钱、加钱与记录日志功能
需要注意一点就是,我们这个案例的预期效果为:无论转账操作是否成功,均进行转账操作的日志留痕。
3.4.2.2 环境准备
该环境是基于转账环境来完成的,在其基础上,我们继续往下写:
a. 创建日志表
1
2
3
4
5
| create table tbl_log(
id int primary key auto_increment,
info varchar(255),
createDate datetime
)
|
b. 添加 LogDao 接口
1
2
3
4
| public interface LogDao {
@Insert("insert into tbl_log (info,createDate) values(#{info},now())")
void log(String info);
}
|
c. 添加 LogService 接口与实现类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| public interface LogService {
void log(String out, String in, Double money);
}
@Service
public class LogServiceImpl implements LogService {
@Autowired
private LogDao logDao;
@Transactional
public void log(String out, String in, Double money) {
logDao.log("转账操作由" + out + "到" + in + ",金额:" + money);
}
}
|
d. 在转账的业务中添加记录日志
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| public interface AccountService {
public void transfer(String out, String in, Double money) throws IOException;
}
@Service
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
@Autowired
private AccountDao accountDao;
@Autowired
private LogService logService;
@Transactional
public void transfer(String out, String in, Double money) {
try {
accountDao.outMoney(out, money);
accountDao.inMoney(in, money);
} finally {
logService.log(out, in, money);
}
}
}
|
e. 运行程序
当程序正常运行,tbl_account 表中转账成功,tbl_log 表中日志记录成功
当转账业务之间出现异常(int i =1/0),转账失败,tbl_account 成功回滚,但是 tbl_log 表未添加数据
这个结果和我们想要的不一样,什么原因?该如何解决?
失败原因:日志的记录与转账操作隶属同一个事务,同成功同失败
最终效果:无论转账操作是否成功,日志必须保留
3.4.3 事务传播行为

对于上述案例的分析:
- log 方法、inMoney 方法和 outMoney 方法都属于增删改,分别有事务T1,T2,T3
- transfer 因为加了
@Transactional 注解,也开启了事务T
- 前面我们讲过 Spring 事务会把T1,T2,T3都加入到事务T中
- 所以当转账失败后,所有的事务都回滚,导致日志没有记录下来
- 这和我们的需求不符,这个时候我们就想能不能让 log 方法单独是一个事务呢?
要想解决这个问题,就需要用到事务传播行为,所谓的事务传播行为指的是:
事务传播行为:事务协调员对事务管理员所携带事务的处理态度。
具体如何解决,就需要用到之前我们没有说的 propagation属性。
a. 修改 logService 改变事务的传播行为
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| @Service
public class LogServiceImpl implements LogService {
@Autowired
private LogDao logDao;
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW)
public void log(String out, String in, Double money) {
logDao.log("转账操作由" + out + "到" + in + ",金额:" + money);
}
}
|
运行后,就能实现我们想要的结果,不管转账是否成功,都会记录日志。
b. 事务传播行为的可选值
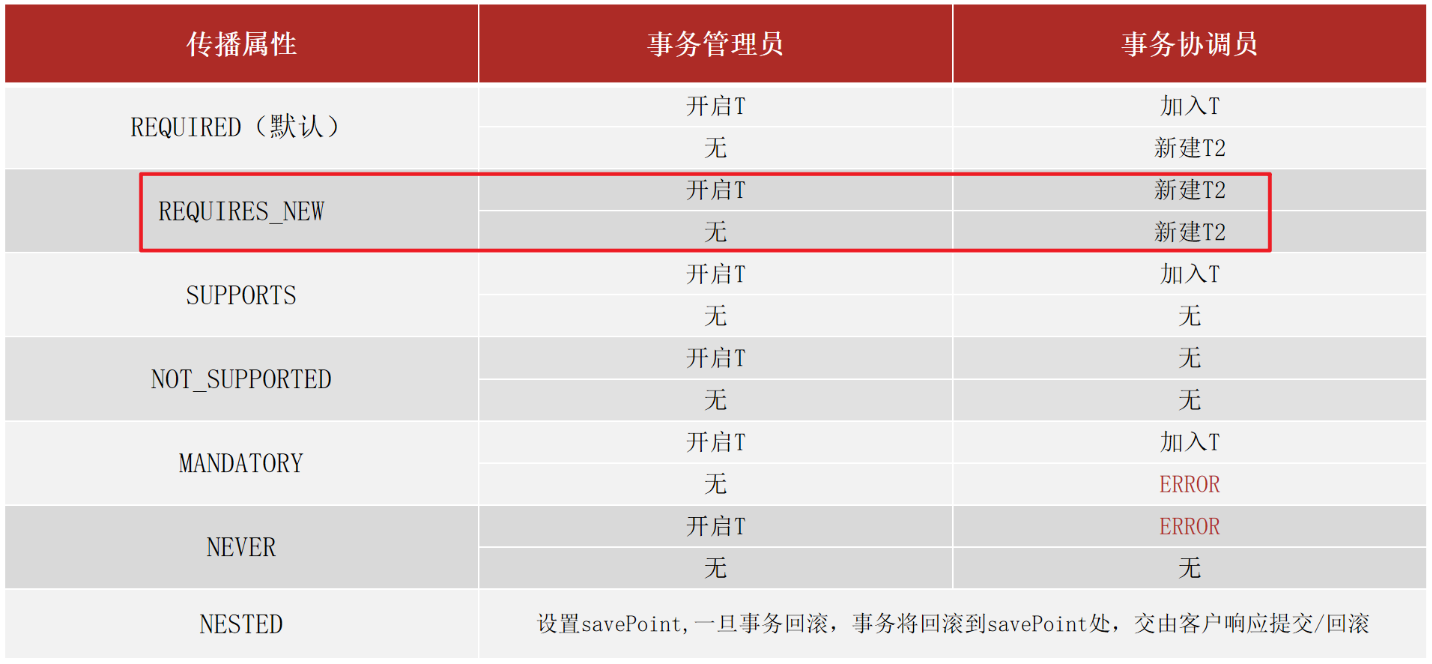
对于我们开发实际中使用的话,因为默认值需要事务是常态的。根据开发过程选择其他的就可以了,例如案例中需要新事务就需要手工配置。其实入账和出账操作上也有事务,采用的就是默认值。















